OPC Library Import Rules
For each combination of data type and direction, the import rules define the object model to be used during the import. By reading the library import rule specified in the configuration file, the point to create is automatically determined.
The name of the data point element to associate with an OPC item is taken from the default property of a specific object model. You can view and modify the default property using the Models & Functions application. The default property must be carefully chosen and its data type must be set to GMS*** to allow the update of the Value attributes with the data contained in the CSV configuration file. It is also possible to specify a different object model by defining its name and the name of the corresponding data point element to associate ([Object Model Property] field in the CSV configuration file).
When you are in Engineering mode and select the OPC import rules in System Browser, the Import Rules tab lets you specify the rules for mapping the OPC types with the associated OPC object models.

The customization of an OPC library will affect the algorithm used to determine the object model and data element to associate with an OPC item during the import. This means that the order in which any customized library or block will be considered is determined by the standard library customization behavior (the most specific library defined for the that project).
The Objects and Properties expander lets you map OPC types and OPC object models: It also lets you define transformation type and the direction of communication for a field point of an object model.
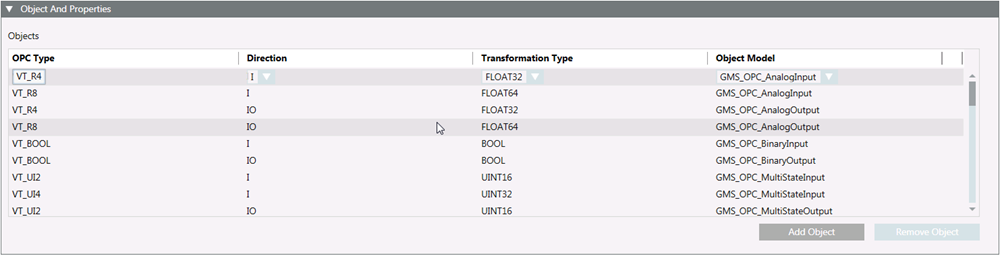
- OPC Type (see OPC Items Data Types, below)
- Direction (see OPC Items Direction, below)
- Transformation Type (see OPC Items Transformation Types, below)
- Object Model
You can modify existing objects or create new objects.
Modifying the import rules may seriously affect system behavior and should always be done by qualified and authorized librarians. Do not modify any of such rules unless you know exactly what you are doing.

The customization of an OPC library to a lower level does not affect the standard import rules (L1-Headquarter). Customized import rules are read and set from the standard import rules; any changes to customized import rules ) do not overwrite standard import rules.
Data Type | Description |
Byte | Unsigned char |
Int16 | 16-bit integer |
UInt16 | 16-bit unsigned integer |
Int32 | 32-bit integer |
UInt32 | 32-bit unsigned integer |
Int64 | 64-bit integer |
UInt64 | 64-bit unsigned integer |
Float32 | 32-bit float |
Float64 | 64-bit float |
Bool | Boolean |
Enum | Enumerative |
String | String |
Time | Date/time |
Byte_Array | Unsigned char array |
Int16_Array | 16-bit array of integers |
UInt16_Array | 16-bit array of unsigned integers |
Int32_Array | 32-bit array of integers |
UInt32_Array | 32-bit array of unsigned integers |
Int64_Array | 64-bit array of integers |
UInt64_Array | 64-bit array of unsigned integers |
Float32_Array | 32-bit array of floats |
Float64_Array | 64-bit array of floats |
Bool_Array | Boolean array |
String_Array | String array |
Enum_Array | Enumerative array |
Time_Array | Data/time array |
Transformation Type String | Data Point Element Type (WinCC OA) |
UCHAR | char |
INT16 | int |
UINT16 | uint |
INT32 | int |
UINT32 | uint |
INT64 | long |
UINT64 | ulong |
FLOAT32 | float |
FLOAT64 | double |
BOOL | boolean |
STRING | string 4096 bytes |
TIME | time |
UCHAR_ARRAY | dyn_char |
INT16_ARRAY | dyn_int |
UINT16_ARRAY | dyn_uint |
INT32_ARRAY | dyn_int |
UINT32_ARRAY | dyn_uint |
INT64_ARRAY | dyn_long |
UINT64_ARRAY | dyn_ulong |
FLOAT32_ARRAY | dyn_float |
FLOAT64_ARRAY | dyn_float |
BOOL_ARRAY | dyn_boolean |
STRING_ARRAY | dyn_string |
TIME_ARRAY | dyn_time |
In the current version of Desigo CC, to modify OPC items of array type and output direction (O) you have to implement a script. See the script example below.
///ApplicationView_Logics_Scripts_ArrayOutput.ArrayOutput.v=0_0.b=3_0_0038_0.10001.Array Output.
// Strict mode makes it easier to write "secure" code, introducing better error-checking
'use strict';
/*
* Press CTRL+Space for suggestion on the commands you can use.
* Press F1 for additional help and for a list of examples.
*/
//StringArrayOutput
executePropertyCommand("System1.ManagementView:ManagementView.FieldNetworks.OPC_Net.Server_Softing.Group_Output.String_Array_Output","Value","Write",["SAMPLE TEXT1","TEST2","STRING3"])
//AnalogArrayOutput
executePropertyCommand("System1.ManagementView:ManagementView.FieldNetworks.OPC_Net.Server_Softing.Group_Output.R8_Array_Output","Value","Write",["-3.1","1","0"])
executePropertyCommand("System1.ManagementView:ManagementView.FieldNetworks.OPC_Net.Server_Matrikon.Group_3.AnalogOutput1","Value","Write",["3.1","1","0"])
//IntArrayOutput
executePropertyCommand("System1.ManagementView:ManagementView.FieldNetworks.OPC_Net.Server_Softing.Group_Output.INT_Array_Output","Value","Write",["245","-567","100000"])
//DateArrayOutput
var a = new Date(2017,5,5,16,26,40,500)
var b = new Date(2018,6,6,16,26,40,500)
executePropertyCommand("System1.ManagementView:ManagementView.FieldNetworks.OPC_Net.Server_Softing.Group_Output.Time_Array_Output","Value","Write",[a, b])
console(a)
console(b)
//CharArrayOutput
executePropertyCommand("System1.ManagementView:ManagementView.FieldNetworks.OPC_Net.Server_Softing.Group_Output.UI1_Array_Output","Value","Write",["d","e","c"])
Direction string | Description |
I | OPC tag parameterized as Input (readable in the OPC server). |
O | OPC tag parameterized as Output (writable in the OPC server). |
IO | OPC tag parameterized as Input/Output (readable and writable in the OPC server). |
